Why AI hallucinates and why it matters!
Ankur Taly, scientist at Google
Watch Now
13:03 Minutes The average reading duration of this insightful report.

Reusable rockets & satellite miniaturization collaboratively are democratizing access to space. Fuelling innovation across multiple domains and fostering a future where space is accessible to enterprises, individuals, and nations alike.
Explore a sneak peek of the full content
The section delves into the historical roots of the space race between the United States and the Soviet Union, highlighting its profound impact on technological advancements. It explores how the competition between these superpowers catalyzed innovations that have become essential in various industries, including telecommunications, healthcare, and more. The section also discusses how the end of the space race didn’t mean the end of innovation but rather heralded a new era of technological advancements that continue to shape our world today.
This section focuses on the economic revolution brought about by the introduction of reusable rockets. It discusses how companies like SpaceX have drastically reduced the cost of space exploration by developing rockets that can be landed and reused. This has made space more accessible to not just governments but also private entities and educational institutions, thereby democratizing space exploration. Download Complete Research
The Aerospace Security Project (ASP) in Sept ‘22 conducted an analysis of the cost of payload launches throughout history. The cost of heavy launches in LEO have been reduced by almost 95% from $65,000 to $1,500.

The section provides an in-depth look at SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket, one of the most iconic reusable rockets in the industry. It discusses its design, capabilities, and the groundbreaking technology that allows it to be reused, making space travel more economical and sustainable. The Falcon 9 serves as a case study for the potential future of cost-effective space exploration.
This section explores the trend of miniaturization in satellite technology, focusing on the development of CubeSats. These small, modular satellites have opened up new avenues for space exploration and commercial applications. Their smaller size and modular design make them more cost-effective and accessible, allowing for a wider range of applications and participants in space technology. Download Complete Research
The section discusses how CubeSats are revolutionizing agriculture by providing high-resolution imagery of farmland. This technology enables more efficient and effective resource allocation, transforming traditional farming methods. CubeSats are making precision farming more accessible, allowing for optimized use of water, fertilizers, and workforce, thereby making farming more sustainable and cost-effective.

This section delves into the additional innovations that CubeSats have enabled, beyond their initial applications. It discusses how these small satellites serve as testbeds for new technologies and scientific research, from studying Earth’s atmosphere to testing new materials and communication technologies. CubeSats are paving the way for future advancements in space technology. Download Complete Research
The section explores the emerging business models in the space industry, particularly focusing on the ‘As-a-Service’ models. It discusses how these models are making space technology more affordable and accessible, from Data-as-a-Service to Mission-as-a-Service. These new business models have the potential to further democratize space technology, making it accessible to a broader range of participants.
Credits
Authors@lab45: Abhigyan Malik
Key contributors: Ariel Zajdband, Planet

10:24 Minutes The average duration of a captivating reports.

GenAI is changing the banking industry through work automation, individualized customer experiences, and fraud detection. Operational cost savings from using GenAI chatbots in banking globally is 35 times more than not using GenAI. GenAI helps banks increase productivity, lower expenses, and enhance customer happiness.
Among industries globally, GenAI could add about $ 3.5 trillion annually in productivity on average, out of which the banking sector would be nearly 8 per cent. Banks are starting with applications in software development, chatbots and media content generation. GenAI has vast potential to execute business and technology processes autonomously. The operational cost savings from using GenAI chatbots in banking reached $7.3 billion globally. It is 35 times the operational savings without using GenAI. The integration of GenAI with virtual assistants has significantly enhanced customer support and experience. GenAI enables banks to automate crucial processes such as customer onboarding, fraud detection, and risk management. As a result, employees can concentrate on more intricate tasks, such as delivering exceptional customer support. The banking sector can significantly benefit from this, leading to an overall increase in efficiency. Download Complete Research
Empowering customers through GenAI
Corporate banking, retail banking and software engineering are the most value-creating functions with each providing a value of about $ 50 billion. The rest of the functions include wealth management, asset management, risk, IT and finance and HR. Download Complete Research
The diagram below shows the impact of GenAI on banks' functional architecture
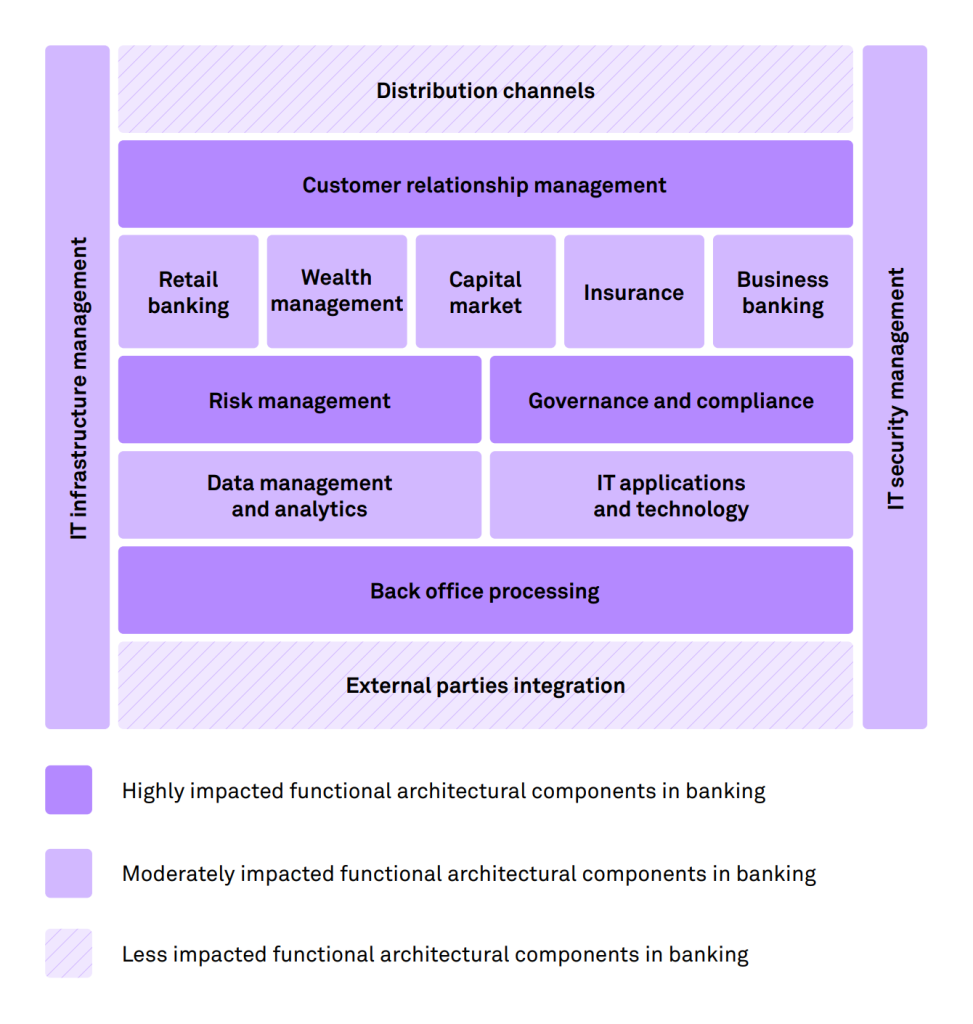
GenAI is in nascent stage, but it has the potential for vast changes in banking. The following use cases are expected to prevail in future:
Credits
Author@lab45: Poonam Pawar, Hussain S Nayak

13:30 Minutes The average duration of a captivating reports.

GenAI is transforming various domains including software engineering. This technology enables high productivity, rapid development, and abundant innovation promising overall productivity gains of 26-30%. Embrace the future and discover the extraordinary potential of GenAI.
GenAI is expected to boost productivity in software engineering by 28% and is projected to improve task completion speed by 54% by 2025. It can also increase application development and maintenance revenue by 25%-30%, leading to a 5%-6% improvement in overall profitability. The GenAI market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 42% over the next decade, and the technology can help address the expected shortfall of 4 million developers by 2025. However, detailed study and implementation strategies are needed to consider factors such as initial installation effort, resource training, and technology integration.

GenAI can significantly impact the various phases of software development by generating code, improving code quality, simplifying code structures, and automating tasks such as unit testing and bug detection. It can reduce the duration of task execution across various software development stages by 20%-45%, resulting in substantial cost savings. While software engineers may be the primary beneficiaries of GenAI, other teams, such as architects, consultants, and sales teams, can also derive substantial advantages. However, implementing GenAI requires a comprehensive strategy that includes tool selection, investment, deployment, and developer training. The implementation strategy should target the highest-leverage phases of software development, and enterprises should invest in resources and training necessary for developers to leverage the technology effectively. Download Complete Research
Integration of GenAI with DevOps principles can increase productivity by automating tasks, generating content, and providing intelligent insights. Adopting GenAI in the DevOps software development environment can further boost productivity through script generation, automated monitoring and alert generation, and synthetic data for pipeline load testing. GenAI can complement and enhance Low Code No Code (LCNC) capabilities by integrating visual developer interfaces, quickening development cycles, and creating text and multimedia assets. Key platforms for code generation using GenAI include Copilot by GitHub, CodeWhisperer by AWS, ChatGPT by OpenAI, Vertex AI by Google Cloud, and TabNine by Codota Dot Com Ltd.

As AI continues to evolve, GenAI will become an increasingly essential aspect of the software development process. GenAI provides opportunities for innovation and creativity while also presenting new challenges. Customized benchmarking contextualized to the customer environment is crucial in refining and optimizing GenAI tools, fostering greater productivity and efficiency in software development. Enterprises must formulate a comprehensive GenAI strategy and incorporate GenAI tools in the implementation and testing phases of the software development lifecycle to maximize development cost and effort savings and improve quality. Collaboration with GenAI tools will create new roles, such as Prompt Engineers, and allow developers to focus on strategic thinking and creative problem-solving. GenAI is also an excellent learning and training tool, automating the generation of educational content and assisting in information retrieval and organization. Download Complete Research
Credits
Lead Authors@lab45: Hussain S. Nayak, Anju James
Contributing Authors@lab45: Vinay Ramananda, Dattaram B A
This is your invitation to become an integral part of our Think Tank community. Co-create with us to bring diverse perspectives and enrich our pool of collective wisdom. Your insights could be the spark that ignites transformative conversations.
Learn MoreKey Speakers
Thank you for subscribing!!!
