Leading the AI transformation of your company
Prof. Gregory LaBlanc, Lecturer, Haas School of Business and Berkeley Law
Watch Now
28:38 Minutes The average reading duration of this insightful report.

Platform ecosystems are defined as open or closed networks where an orchestrator mediates relationships between a diverse set of complementary stakeholders. Orchestrators receive benefit from both accrued value in the platform ecosystem and in barriers to entry that ecosystems create for potential competitors. Platform ecosystems are also defined by a collaborative strategy that aims to create value for all stakeholders, including customers, partners, suppliers, and competitors.
Explore a sneak peek of the full content
Platform ecosystem business models (platform ecosystem) have evolved in response to expanding business interconnection and complexity. They depart from traditional business models that emphasize internal control and efficiency. They establish and utilize connections with ecosystem stakeholders, who are independent actors, to produce value. They aim to establish a network effect that produces more value than any single entity could provide. Download Complete Research
They, ideally, conduct the following:
The essential elements of ecosystem business models are:
Suppliers(n): Businesses or institutions that provide the materials, components, or logistical support.
Orchestrator(Only one): Coordinates and controls the interactions between various ecosystem participants, such as suppliers and complementors, to add value for customers and foster the ecosystem’s overall growth.
Complementors(n): Offer additional goods or services to the orchestrator’s offers.
Customers(n): End-users or beneficiaries.
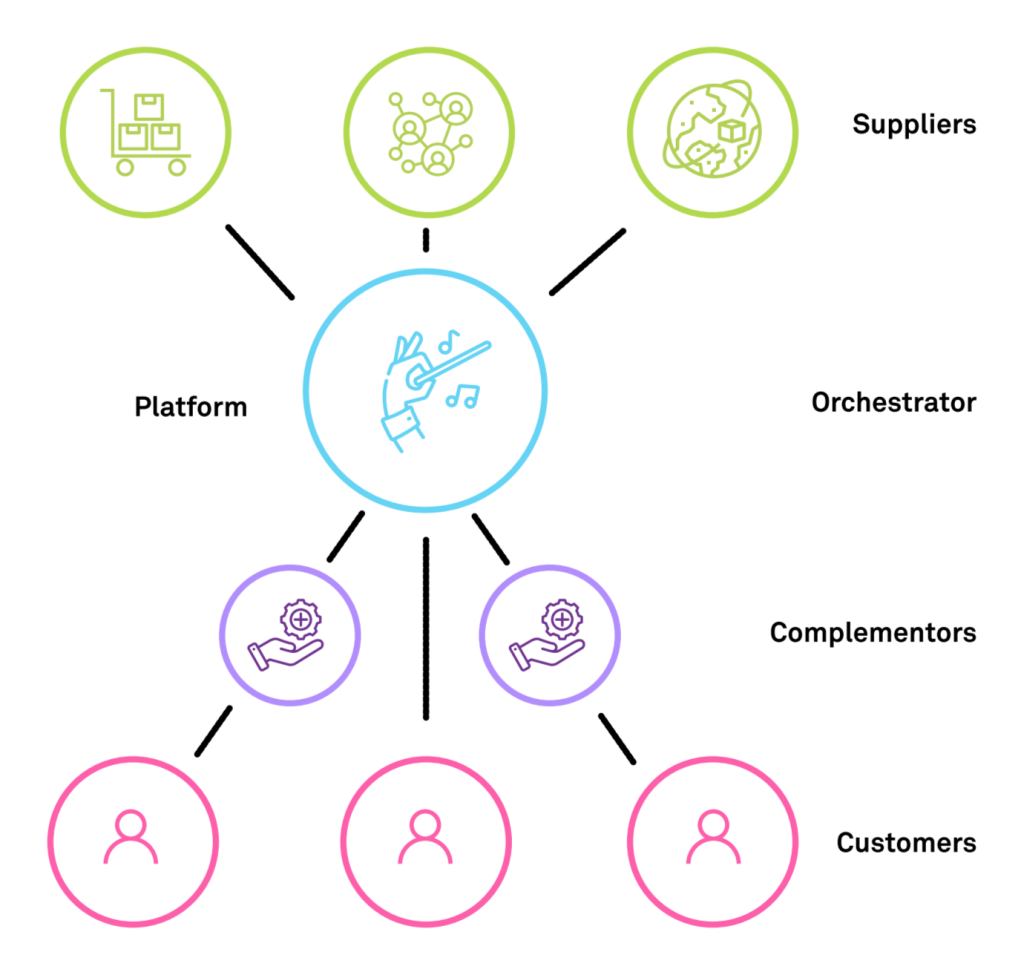
Ecosystem platforms rely on network effects to grow and prosper since they boost the platform’s value as more users join and interact with the ecosystem. Network effects create a positive feedback loop that improves the overall value proposition is created as the user base expands and draws in new developers and enterprises to offer their services. Download Complete Research
Today, organizations across industries are exploring the potential of ecosystems to create additional value and minimize capital-intensive internal processes.
The business landscape is now characterized as the “age of business ecosystems,” where enterprises that adopt ecosystems are better positioned to drive innovation and capital efficiency, and thus create more value for customers.
Partnership ecosystem: Partners within an organization work together to realize common objectives, capitalize on one another’s advantages, and co-create value.
Examples: Disney-Marvel, Amazon-Whole Foods Market
Aggregator marketplace ecosystem: A platform-based environment that brings together a variety of suppliers and buyers, facilitating transactions and generating value for all parties.
Examples: Amazon, Airbnb
Growth/expansion ecosystem: This ecosystem gives firms the resources to grow their operations and penetrate new markets. Resources include capital, knowledge, collaborations, and infrastructure.
Example: Uber expanding to Uber eats
Orchestrator ecosystem: A platform or network that facilitates transactions between ecosystem partners. In addition to setting up the infrastructure and tools needed for participants to work together and add value, the orchestrator also defines rules, standards, and protocols.
Example: AWS marketplace
Supply chain ecosystem: Enterprises leverage their existing capabilities (value chain ecosystem) to create an ecosystem of suppliers and partners to support their operations and growth.
Example: Apple’s supply chain ecosystem, Dell’s Direct Model
Community-based ecosystem: Businesses that are create social and environmental impact alongside financial goals.
Examples: Amul, Patagonia
Crowdsourcing ecosystem: Ecosystems that enable individuals to collectively contribute their knowledge, skills, and resources towards solving problems, generating ideas, or completing tasks.
Example: OpenStreetMap, Kickstarter
Technology/Innovator platform-based ecosystem: Ecosystem of interconnected IT resources that can function as a unit. Comprised of suppliers, customers, applications, and third-party service providers.
Example: SAP platform, Apple iOS ecosystem
Ecosystem orchestrators create strategic partnerships and alliances to connect companies in a value chain.
They offer products and services that are mostly limited to their original product range and they share customers and data with their partners.
Orchestrators connects various stakeholders and create shared value for an ecosystem community.
They take on the risk, complexity, and challenges of supporting stakeholders. They enable others to create and sell goods and services through their ecosystem platform. They maintain a high level of quality within their ecosystem. Download Complete Research
Their roles are as follows:
Platform ecosystem business models have proven to be a powerful modality, both for creating value and fostering collaboration among stakeholders.
Niche players in emerging industries may find it challenging to participate in global transactions or initiatives independently, but when positioning themselves within the ecosystem they can leverage the broader ecosystem’s resources or network effect to engage in larger endeavours and expand their customer reach.
Larger enterprises that struggle with agility in producing niche goods can benefit from partnerships with more nimble businesses within ecosystems. They can gain access to specialized knowledge and capabilities that enable them to deploy innovative products to market at speed.
As technology continues to reshape businesses and economies, the importance of platform ecosystem business models are expected to grow. Competent management of platform ecosystems will be a defining characteristic of successful leadership teams. Platform ecosystem owners can enhance their operations and user experience by establishing effective feedback channels. Download Complete Research
Credits
Author@lab45: Poonam Pawar
Contributing Author: Hussain S Nayak

40:28 Minutes The average duration of a captivating reports.

In today's fast-paced business landscape, staying ahead requires more than just keeping up with the latest trends—it demands innovation. This is particularly true in the realm of BPS, where efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability reign supreme. In our latest special report, we delve into the transformative power of GenAI and its profound implications for the future of BPS.
What's Inside
In today's fast-paced business landscape, staying ahead requires more than just keeping up with the latest trends—it demands innovation. This is particularly true in the realm of Business Process Services (BPS), where efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability reign supreme. In our latest special report, "Business Process Services in the Era of Generative Artificial Intelligence," we delve into the transformative power of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) and its profound implications for the future of BPS.
We analyze the current state of BPS, highlighting its strengths and limitations. Traditional approaches have undoubtedly improved operational efficiency, but they often fall short in handling complex tasks that require nuanced decision-making and adaptability.
Enter Generative AI—a game-changer in the world of BPS. We explore how GenAI offers innovative solutions to longstanding challenges, from streamlining repetitive tasks to enhancing decision-making processes. By harnessing the power of machine learning and natural language processing, GenAI empowers organizations to automate workflows, optimize resource allocation, and drive unprecedented levels of efficiency.
Navigate hurdles of GenAI adoption with strategies for data governance, technical integration, and fostering a culture of AI acceptance. Our paper equips readers to overcome obstacles, ensuring successful implementation and maximizing the transformative potential of AI in BPS.
We delve into how GenAI is reshaping BPS as we know it. From revolutionizing customer service with chatbots to automating document processing tasks, the potential applications are limitless. By augmenting human capabilities with AI-driven insights, organizations can elevate their BPS capabilities to new heights, unlocking untapped value and gaining a competitive edge in the process.
But how do we quantify the financial impact of GenAI adoption? We explore this question in detail, outlining key metrics and methodologies for assessing ROI. Whether it is through cost savings, revenue generation, or enhanced customer satisfaction, the benefits of GenAI are tangible and far-reaching.
Looking ahead, we paint a compelling picture of the future of BPS with GenAI at its core. As organizations embrace AI-driven automation and innovation, we envision a landscape where BPS becomes synonymous with efficiency, agility, and strategic value creation. By leveraging GenAI to its fullest potential, businesses can future-proof their operations and thrive in an era of unprecedented digital transformation.
" Business Process Services in the Era of Generative Artificial Intelligence " offers a comprehensive exploration of the transformative potential of GenAI in the realm of Business Process Services. From addressing current challenges to envisioning future opportunities, this paper serves as a roadmap for organizations looking to harness the power of AI to drive meaningful change and unlock new possibilities. Join us on this journey as we redefine the future of BPS together.
Credits
Author@lab45: Ankit Pandey

22:23 Minutes The average duration of a captivating reports.

Think your enterprise can be a leader without a well-thought business? A business model is necessary for you, as an enterprise leader, to scale your ideas, products, and services and sustain them. Here's your roadmap.
Innovative technologies and novel approaches to conventional business practices are expected to drive business models in the future. Platform-based business models powered by AI, cloud computing, and blockchain are predicted to improve efficiency, streamline operations, and create new revenue streams. Immersive technologies and eco-friendly practices in the experience and creator economy enhance user engagement and provide new monetization opportunities. The machine and API economy leverage AI and automation to reduce operational costs and ensure ethical and responsible use. Platform ecosystems are also expected to support innovation and be built around data platforms used by organizations, customers, vendors, and other stakeholders. Download Complete Research
To stay ahead in today's market, enterprises must navigate market dynamics, consumer behavior, and technological advancements. A comprehensive business model is critical to their performance, optimizing operations and generating additional revenue sources. It should identify the target audience, market segment, and describe products or services while developing strategies for marketing and sales, assessing costs, risks, and profitability. Platform-based models powered by AI, cloud computing, and blockchain will streamline operations and create new revenue streams. Innovative technologies and eco-friendly practices will enhance user engagement, providing new monetization opportunities while leveraging AI and automation to reduce costs.
Several business models have emerged based on specific business needs, including e-commerce, subscription, freemium, marketplace, franchise, and direct sales. Each model has unique features and advantages and may overlap with other business model features. Choosing a suitable model can help an enterprise to succeed in a competitive market. Based on research by Wipro Lab45, business models can be categorized based on various parameters such as distribution, licensing, target audience, and technology. We have classified them into six broad categories, as listed below. Most enterprises today follow one or a combination of these models based on their strategic priorities, customer preferences, market demand, and profitability. The categories mentioned are not exclusive but are the most popular. Download Complete Research
Business model strategy refers to the design and development of the business model to create, deliver, and capture value for its customers, while achieving its overall enterprise goals and objectives. Enterprise can create a business model plan that considers all its main business model components, aligns with its aims and objectives, and changes with the market over time by following the eight phases stated below, with interactive and incremental models.
Enterprises that have thrived in the last decade have embraced novel methods to create value and gain a competitive edge. One such method is the ecosystem business model built on a digital platform. Successful ecosystem business models are founded on mutual benefit, co-creation, and collaboration. By focusing on these elements, companies can build a healthy ecosystem that delivers unique value propositions and promotes sustainable growth. Amazon and Airbnb are good examples of prosperous business ecosystems that have used these success criteria. By leveraging technology and data, successful firms have improved efficiency, created new revenue sources, and maintained a competitive edge... Download Complete Research
Credits
Author@lab45: Hussain S Nayak, Poonam Pawar
This is your invitation to become an integral part of our Think Tank community. Co-create with us to bring diverse perspectives and enrich our pool of collective wisdom. Your insights could be the spark that ignites transformative conversations.
Learn More

Key Speakers
Thank you for subscribing!!!
