Are LLMs the Answer to Everything
Prof. Mausam, IIT Delhi
Watch Now
14:33 Minutes The average reading duration of this insightful report.

Digital identity systems have evolved and continue to evolve. They are core to our interactions with the digital world and have made great strides in both security and convenience. However, the privacy and data-use consent of identity-holders remain problematic.
Explore a sneak peek of the full content
We have seen Digital Identity evolve from the silo identity model to the federated identity model. The current systems reside at a very low trust level, with over 93% of users distrusting social media platform’s digital custodianship. We believe the next stage of evolution will be Decentralized Identity
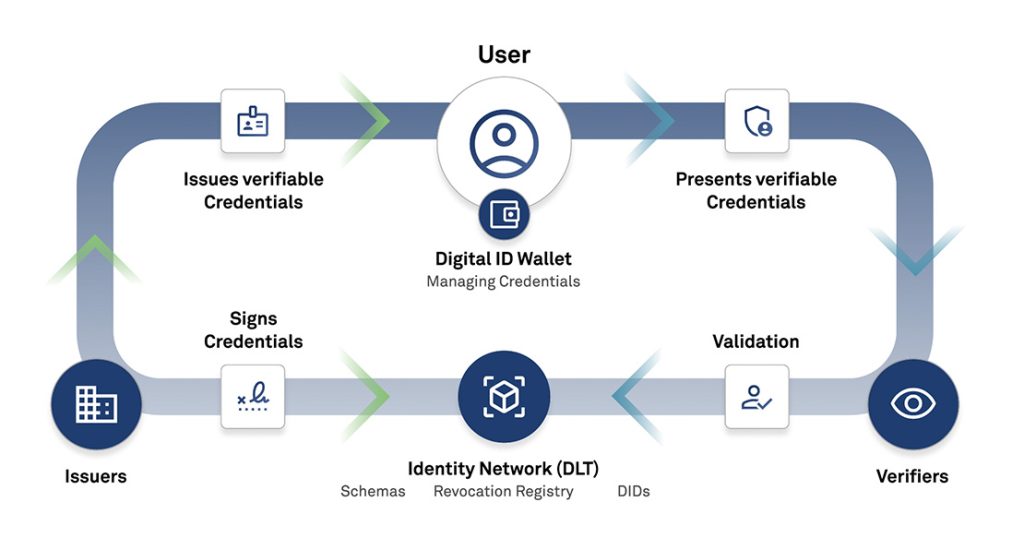
Web 3.0, the internet’s next evolution aims for a decentralized interconnected and intelligent web. It aims for decentralized, peer-to-peer networks for secure, trustless transactions— without intermediaries. Unlike today’s static web that does not adapt to the needs of its users, Web 3.0 will be dynamic and interactive, leveraging AI and blockchain to personalize, adapt, and democratize the internet. As user identity is crucial in Web3, DID will be foundational. We explain the ecosystem and functionality of the DID network. Download Complete Research
User benefits include credential forgery prevention, password-free authentication, spam prevention and many others. While Organizations will benefit from operational cost reduction and security cost reduction, enhanced user experience thereby improving the brand. Organizations must however use a phased approach to implement, which is explained.
We identify four key obstacles that present themselves and what organizations can do to overcome them.
The global decentralized identity market was valued at $285 million in 2022 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 88.7% over the next 5 years. We evaluate top players and products in the market and how they have helped the technology evolve. Download Complete Research
Credits
Author@lab45: Sujay Shivram, Abhigyan Malik

11:39 Minutes The average duration of a captivating reports.

By acquiring 100+M users in first 3 months of launch, ChatGPT has brought the field of Generative AI (GenAI) into mainstream awareness. The adoption of ChatGPT and similar applications have positioned Generative AI (as well as “Deep Learning”) as the newest disruptive tech after cloud computing.
Generative AI, a field of Artificial Intelligence, refers to computational models that are trained on massive amounts of input data (300bn words in the case of ChatGPT). They can synthesize data, draw inferences and create new outputs in the form of text, images, video, audio, new data and even code.
Two architectures have made GenAI immensely valuable
ChatGPT, for instance, uses the transformer model along with Human Feedback Reinforcement training to generate high quality outputs. Training a model requires intensive computational power (supercomputers were used to train GPT3) and significant investments (OpenAI being a key example). But once a model is trained, it can be optimized for a larger user base. Download Complete Research
The market is expected to grow from $8B in 2022 to $109B in 2030 at a CAGR of 34.6%. Key facts as follows
Need for content synthesis
We generate ~2.5 quintillion bytes of data every day on the internet. This not only makes searching for information tough but also makes inferring tougher, for regular users. GenAI tools can search, synthesize and compose an answer.
Democratization of content creation
We are moving from a search and retrieval economy to an infer and compose economy. People used to prompt algorithms to search and retrieve information but now they can prompt algorithms to infer and compose information.
Instant economy
Digital natives prefer tools that enable instant creation of content e.g. Tik Tok. ChatGPT can generate a word in 350ms after processing database of 300B words.
Access to massive computational power
The ability to instantly process and compose information using cloud computing.
Evolution of deep learning neural networks
Large Language Models have become openly available. These models help organize much of the internet’s information and develop patterns to mimic human decision-making.
Download Complete Research
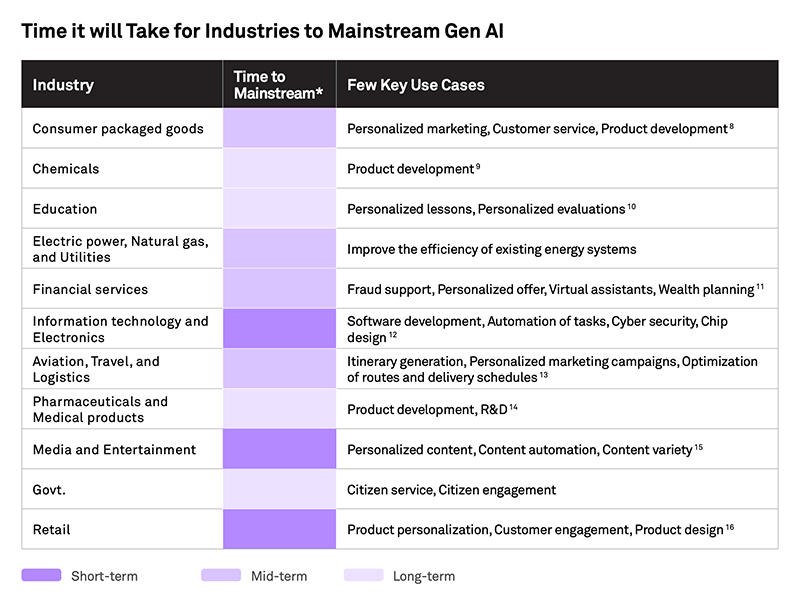
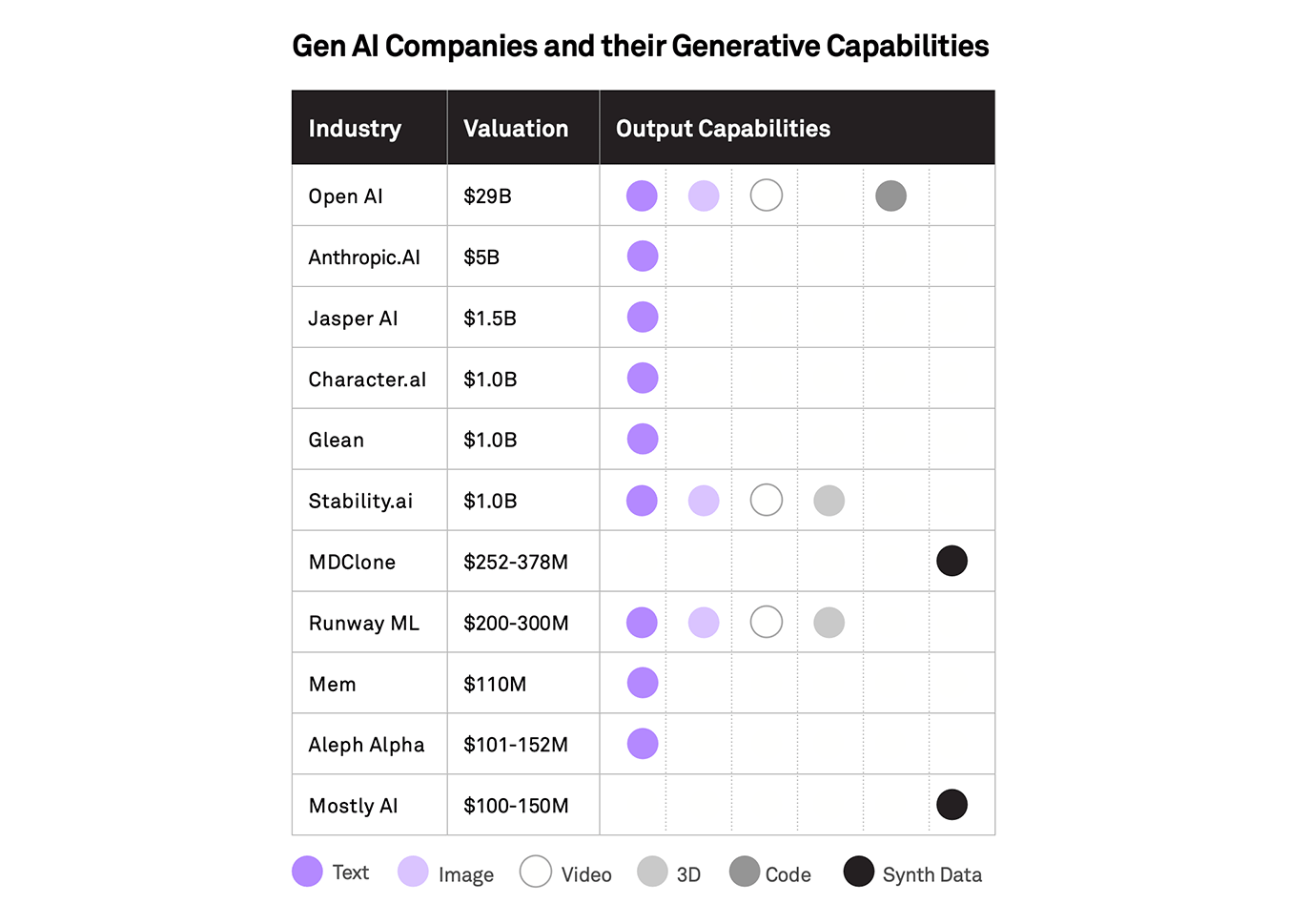
GenAI will fundamentally change several functions in enterprises leading to improved productivity and performance of employees. A Few areas of business where it will have the biggest impact are as follows:
Content creation
Gen AI will lead to more automation in content creation. It will not only reduce the cost of content creation but also increase the quality & variety of content created. Generative AI based DIY Apps are expected to emerge for marketing and design functions.
Content personalisation
Marketing touchpoints like newsletter, websites, videos, metaverse etc. will get hyper-personalized. This will improve brand engagement and conversion ratio of the sales funnel.
Drug discovery
Drug Discovery is a time-consuming process that can extend to 5-12 years. Gen AI can help identify potential drug candidates and test their effectiveness using computer simulations, thus saving time in the process. It has already led to tremendous real-world value, when the first mRNA covid vaccines were developed by programming mRNA molecules to express the specific antigen response. By 2025, more than 30% of new drugs and materials could be systematically discovered using GenAI techniques, up from zero today.
Software development
IT products and services could see the biggest impact. Below are some scenarios that may unfold.
Credits
Lead Authors@lab45: Siddhant Raizada, Nagendra Singh, Tommy Mehl, Arvind Ravishunkar
Contributing Authors: Aishwarya Gupta, Anindito De

14:40 Minutes The average duration of a captivating reports.

Foundational for identity verification and rights access, government-issued IDs face breaches and inefficiency within centralized systems. Enter Decentralized Identity solutions, redistributing verification control to individuals. But is it applicable for equally for all government services?
Decentralization of government-issued IDs is a complex issue with potential benefits and drawbacks. Whether government issued Ids should be decentralized or not depends on various factors that we delineate. Any decision on decentralization should be carefully considered and implemented with caution to ensure that they do not breach security or undermine the government’s programs. Download Complete Research
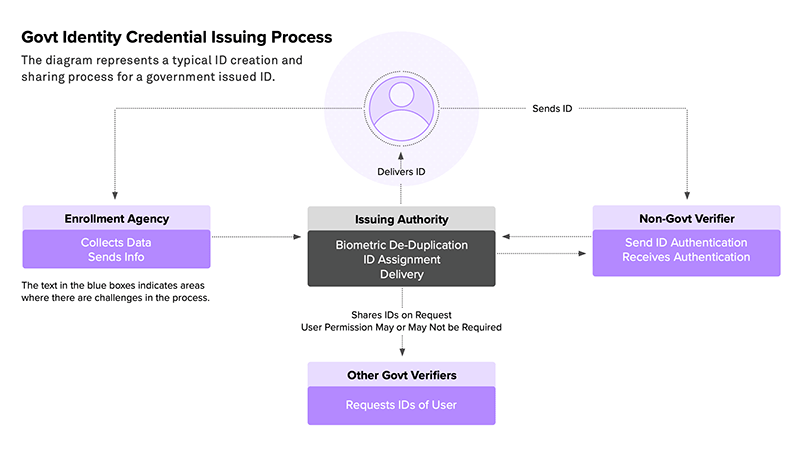
We detail out the current Issuing process typically followed by governments today and identify several challenges and issues that face it today. This includes Ids like the Passport, Licenses, Voter cards and Social security cards. All of them are critical and everyone can do with an easier and more fool proof process for the same.
We evaluate the different government functions such as Education, healthcare, elections, security, taxation, etc and analyze which of these would be most suitable to be decentralized. We map them on a matrix of Complexity & Coordination and the Need for scrutiny to give us an easy framework for assessment. Download Complete Research
We end by considering the long term onjectives and intended outcomes of such an exercise.We feel that Decentralized Identity solutions can rebuild trust in public institutions by empowering residents with data control.
Credits
Author@lab45: Sujay Shivram, Abhigyan Malik
This is your invitation to become an integral part of our Think Tank community. Co-create with us to bring diverse perspectives and enrich our pool of collective wisdom. Your insights could be the spark that ignites transformative conversations.
Learn MoreKey Speakers
Thank you for subscribing!!!
